Request Appointment
Enter your details and we will be in touch with you shortly;
Or call
8655885566
between 8 am and 8 pm.
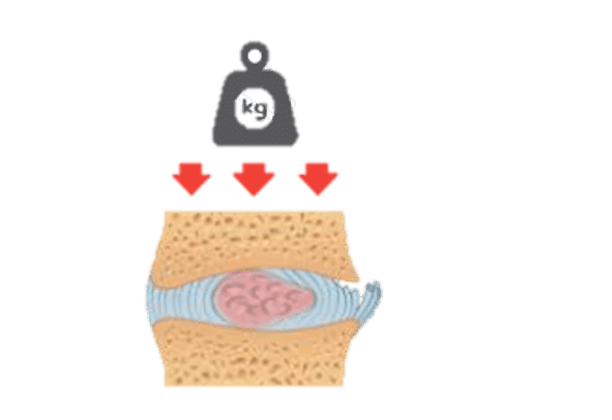
Discs are the shock absorbers of the spine. When part of the disc breaks away from the parent disc at the site of extrusion it is known as disc sequestration
Disc sequestration is a most severe form of disc herniation, also known as a free disc fragment, in which the nucleus pulposus separates and moves into the spinal canal. It may stay free in the epidural space, cause direct compression of the nerve roots, and generate severe manifestations.
For this reason, the fragment is no longer contained, as it often causes more nerve irritation than contained herniations. MRI is considered the best tool for confirming the diagnosis and identifying the position of the free disc fragment.
When conservative measures fail, specialized disc sequestration treatment may be required to remove the fragment and relieve nerve compression. Disc extrusion management protocols in selective cases guide the choice between surgical and non‑surgical approaches.
The main symptom of disc sequestration is pain in the affected area and/or the legs. The extruded material within the disc can press against the spinal nerves, affecting sensory signals from other body parts. Some of the most common symptoms of disc sequestration include:
Conservative management often begins with analgesics, gentle mobilization, and disc sequestration relief therapy to reduce inflammation and improve mobility. In case of symptom continuation and neurological deficit aggravation, the patient should use nonsurgical disc treatment, including physical rehabilitation and exercises.
Surgical decompression is advised mostly for patients who do not respond to conservative treatment. The surgery aims to free the nerves to regain their function and relieve pain. At QI Spine, surgery is the last option. Over 90% of patients advised to undergo surgery elsewhere recovered fully with QI Spine’s non-surgical medical recovery program.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 12 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 12 weeks of QI Spine TherapyThe main cause of disc sequestration is disc degeneration. Disc degeneration decreases the disc’s flexibility, increasing the risk of damage caused by strain or injury. Some of the primary causes of disc sequestration include:
Disc sequestration is where an element of the nucleus pulposus herniates and moves into the spinal column, thus causing nerve inflammation. Key risk factors include:
Recognizing these factors early allows healthcare providers to recommend targeted disc sequestration therapy, which can slow progression and reduce symptom severity.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyNonprescription medicine can treat mild to moderate pain according to your provider’s advice.
These agents relieve pain and inflammation without a prescription. However, specific measures should be taken to avoid adverse effects such as gastrointestinal irritation or liver stress.
If nerve inflammation is the cause of your pain, medications that affect the way your nerves work can be helpful:
These medicines control excessive signals within the brain but may cause side effects like dizziness, dry mouth, and sleepiness.
Recommended for spasticity, the well-known drugs are cyclobenzaprine and methocarbamol.
The compound should only be used as recommended to avoid developing severe sleepiness.
Reserved for a few cases that have not shown any improvements after the other treatments, short-term opioids contain:
Since it may produce dependence and side effects such as nausea, constipation, confusion, and others, opioids are used minimally and cautiously.
If oral medications are ineffective, potent anti-inflammatory agents can be injected around the spinal nerves.
Combining with physical rehabilitation provides specific disc sequestration relief therapy and enhances functional rehabilitation recovery.
A sequestered disc is a disc in which a piece of the nucleus pulposus has migrated fully into the spinal canal and is more liable to require surgical treatment than contained herniations. Suppose the fragment continues to be a source of unremitting radicular pain, severe nerve root compromise, or neurological compromise, including weakness, sensory change, or cauda equina syndrome. In that case, microdiscectomy of the fragment is necessary.
However, there are only mild symptoms and no features of worsening neurological deficit. In that case, the patient may be managed conservatively with regular follow-up, physiotherapy, pain management, and close observation only. Surgery is always done with consultation of the spine specialist. It is considered when non-surgical management has not worked or the patient requires an urgent surgery to relieve compression.
Disc sequestration often causes extreme pain as the sequestered portion of the disc presses against nearby nerves. Conventional treatment for a sequestered disc involves one or more pain killers, including NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs), opioids, epidural infiltrations, and periradicular infiltrations (CT-guided).
Surgery is often recommended in severe cases. However, many of these medications cause severe side effects, and wide-scale studies show that back surgery is often unnecessary and doesn’t improve outcomes.
Pharmacological and surgical methods are temporary fixes that cause more harm than good. However, QI offers a non-pharmacological therapy called Frequency Specific Microcurrent (FSM) to reduce pain caused by a sequestered disc. This treatment method uses low-level electrical currents to reduce back pain without the risk of any side effects.
This therapy also reduces inflammation and promotes the body’s tissue repair processes. Pain management includes isolated muscle training, extensions, and medical movements focusing on core strengthening. The type of movements included in these therapies will depend on the location of the body parts and the intensity.
85% of all back pain cases do not receive a definite diagnosis and are termed “non-specific.” These patients then opt for a standard treatment plan in which the symptoms are managed, but the primary cause is not treated. However, QI has algorithm-based treatment protocols derived from knowledge over 47,000+ past cases. This ensures patients receive a proper medical recovery program customized to their needs. This unique system focuses on evidence-based methods to reduce disability and pain.
Recurrence is a possible complication after back surgery for disc sequestration. Population studies show that recurrent disc herniation can occur in up to 25% of all cases. QI spine specialists will recommend medical movements for each patient based on a thorough physical assessment. Medical movements help to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, which ensures proper alignment of the spine.
The intensity, frequency, and type of medical movement are based on the patient’s requirements. This therapy ensures that the structures affected by the sequestered disc are not further irritated and that the risk of recurrence is minimal. Back pain that is severe or persistent should never be ignored, as it can aggravate the underlying condition and result in serious problems.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyDisc sequestration often causes extreme pain as the sequestered portion of the disc presses against nearby nerves. Conventional treatment for a sequestered disc involves one or more pain killers including NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs), opioids, epidural infiltrations, and periradicular infiltrations (CT-guided). Surgery is often recommended in severe cases. However, many of these medications cause severe side effects and wide-scale studies show that back surgery is often unnecessary and doesn’t improve outcomes.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyIdentifying disc sequestration is crucial to ensure that the patient receives the proper disc sequestration treatment so as not to cause long-term nerve damage. A systematic approach includes:
With disc sequestration confirmed, a plan from conservative non-surgical disc treatment and rehabilitation with anti-inflammatory management to microdiscectomy is achieved. Involvement of spine specialists and spine-oriented disc sequestration therapy is effective in early nerve regeneration and pain management.
The spine doctor will review your previous medical records, conduct a physical examination, and check for symptoms. A neurological examination might also be performed to check your reflexes, muscle strength, ability to walk, and ability to feel.
If required, you may be asked to get a few imaging tests like X-ray, CT scan, and MRI scan to check which nerves have been affected. The Digital Spine Analysis test analyzes the muscles around the spine, which might have become inefficient, leading to a disc sequestration. Here is how DSA is conducted & its benefits:
After the thorough analysis, the doctor will design a personalized disc sequestration therapy for you. The therapy follows the whole patient's journey, and our spine doctors will guide you from the first day of consultation to post-care. The doctor and you can also track the treatment details over QI Spine’s app. The app also lets you map your exercise routine, schedule your video consultation or in-clinic appointment, and track your recovery progress.
Have a question?
Ask our spine specialists
Who is a QI Spine Specialist?
A QI Spine Specialist is a medical expert with

Dr. Nidhi Sanghvi Shah

Dr. Shital Gaikwad

Dr. Richa Bhatia
9000 hours
of specialisation in treating back and neck conditions
32 hours
of spine physiotherapy specialisation methods in McKenzie concepts, Kinetic control, Neurodynamic solutions, Mulligan’s concepts
500 hours
and 6 months of QI Spine specialisation courses