Request Appointment
Enter your details and we will be in touch with you shortly;
Or call
8655885566
between 8 am and 8 pm.
A condition that weakens the structural integrity of bones and makes them prone to breakage
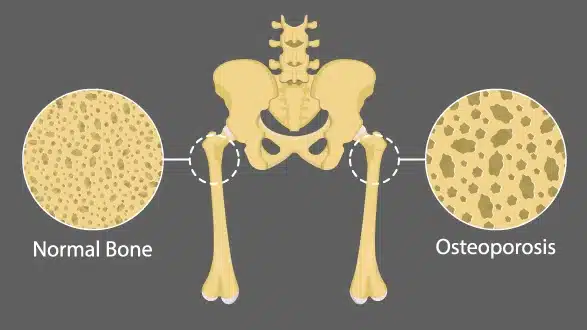
Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the entire skeletal system and is characterized by the thinning, depletion, and weakening of bones, making bones more prone the fractures. Bones become more brittle to the extent that the simple movements, like walking or even the simple stress, like bending or coughing, or any other simple stress, can lead to a breakage of the bone. Lack of vitamin D is one of the major cause behind osteoporosis, and to balance vitamin D, you need to plan osteoporosis treatment under the guidance of a spine doctor.
As the components of the bones gradually break down and become much smaller, bones experience a considerable high stress, including the spinal vertebrae, the femoral neck in the hip, and the distal radius in the wrist, which easily become fractured.
Compression fractures of vertebral bodies result in height loss and Kyphosis, hip fracture leads to disabilities, which may be severe. Since bone loss is a gradual process that may not be accompanied by any symptoms in the early stages, the initial sign is often a minor fracture.
Early osteoporosis treatment focuses on reducing bone loss and strengthening existing bones. This typically involves osteoporosis bone density medication, such as bisphosphonates, alongside lifestyle measures like calcium supplements and weight-bearing exercise. When pain or functional impairment arises, targeted osteoporosis relief therapy, including physical rehabilitation and pain management, helps restore mobility and quality of life.
Due to the slowing down of bone cell generation, bones become brittle and break easily with minimum impact. This condition is called osteoporosis and affects 29% of women between the ages of 30 and 60. However, it could be osteoporosis if you experience:
The data regarding osteoporosis prevalence rate in India is approximately 20–40% in women above 50 years, while in men, osteoporosis prevalence is about 10–20% in the same age group. From the research, some of the causes are a lack of Vitamin D, low Calcium intake in the diet, lack of regular exercise, and others. Early osteoporosis management strategies, such as regular DEXA scans and calcium supplements, are essential to identify at-risk individuals and implement preventive measures before fractures occur.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 12 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 12 weeks of QI Spine TherapyMany causes lead to a gradual loss of bone density. These causes range from hormonal shifts to lifestyle choices, and understanding them is essential for timely intervention through proper osteoporosis therapy. Such therapy should be done early enough since early identification of these triggers results in improved prevention of long-term impairments in bones and decreased possibility of fractures. Don’t ignore the following causes:
Understanding the factors that increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis is crucial for early identification and osteoporosis prevention. Identifying the risk factors allows healthcare providers to recommend appropriate osteoporosis therapy. These risks are divided into four categories as follows:
Recognizing heightened risk can also guide the timing of osteoporosis relief treatment for those who go on to develop low bone mass.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyActive self-care, calcium supplements, vitamin D therapy, and lifestyle management can help improve a patient's condition. It can be controlled by:
Effective osteoporosis treatment aims to reduce bone loss, relieve symptoms, and, in high‑risk cases, stimulate new bone formation. Here are the key medications:
Bisphosphonates are a class of medications used to treat and prevent bone loss, primarily due to osteoporosis and other conditions affecting bone density and strength.
Denosumab injection is a medicine for the treatment of osteoporosis or thinning of bones in postmenopausal women and osteoporosis in men.
Combining these therapies with lifestyle measures, such as osteoporosis relief therapy including weight‑bearing exercises like walking, jogging, running, stair climbing, skipping rope, skiing, and impact-producing sports, optimizes outcomes. These translate to a more effective long-term treatment of fractures since the treatment is customized depending on the patient’s risk factors and bone density.
Following these treatments will help you to get rid of the pain, and it will lead you to recover, but proper guidance from a certified doctor is mandatory. At QI Spine you can consult about your pain by expert spine doctor’s with our free in-clinic or video consultation and that will allow you to expedite your recovery journey.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyThere is no cure for osteoporosis, only active self-care and lifestyle management can help improve a patients condition. It can be controlled by:
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine TherapyAccurate diagnosis of osteoporosis is essential for preventing fractures and guiding appropriate osteoporosis treatment. A structured approach combines clinical evaluation, risk assessment tools, imaging studies, and laboratory tests to confirm low bone mass and stratify fracture risk.
The patient aims to document whether the patient has had any low-impact fractures in the past or a close family member with osteoporosis, and the use of medications like glucocorticoids, which weaken bones.
Assess risks that involve smoking, alcohol consumption, and activity levels of the patient.
For this reason, you should make a physical examination to estimate height, posture, and or vertebral compression.
That is valid for the analysis of the 10-year probability of hip and major osteoporotic fractures that depend on the age, sex, weight, and clinical risk factors.
Helps determine whether to initiate pharmacologic osteoporosis therapy or focus on lifestyle measures.
A gold standard for assessment of BMD at the hip and spine.
In particular, a T-score below -2,5 discriminates osteoporosis, and the score from -1 up to -2,5 points to osteopenia.
Useful for screening in settings without central DXA access.
This test should be accompanied by a DXA scan in the central region in case the results indicate a poor bone mass.
Exclude secondary causes by measuring serum calcium, 25-hydroxyvitamin D level, and parathyroid hormone level.
Evaluate renal and liver function before initiating certain bone density medications.
Bone turnover markers (e.g., osteocalcin, CTX) may help monitor response to osteoporosis treatment.
Usually it is done at the interval of 1–2 years to assess the efficacy of the treatment and disease status.
From the alterations in BMD and fracture frequency, clinicians can boost the intervention and change or add agents accordingly in an attempt to prevent future fractures.
A comprehensive diagnostic protocol, integrating clinical, radiologic, and laboratory data, ensures the timely initiation of effective osteoporosis relief treatment and helps maintain long‑term skeletal health.
After the thorough analysis doctor will develop a personalized osteoporosis therapy for you. The therapy follows the whole patient's journey, and our spine doctors will guide you from the first day of consultation to the post-care. Also, the doctor and you can both track the treatment details over QI Spine’s app. The app also allows you to map your exercise routine, schedule your video consultation or in-clinic appointment, and track your recovery progress.
 Professional diagnosis required
Professional diagnosis required Chronic, can last for years
Chronic, can last for years Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy
Treatable with 4 weeks of QI Spine Therapy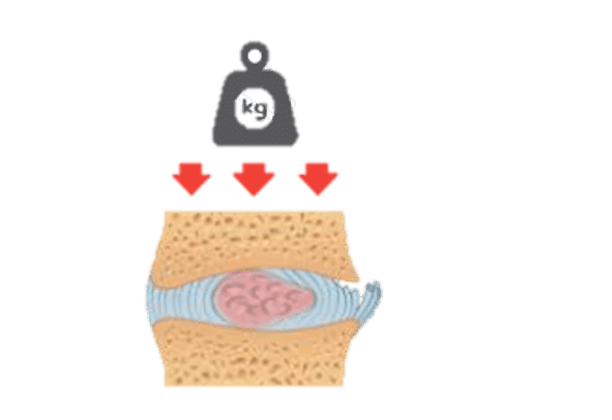
Have a question?
Ask our spine specialists
Who is a QI Spine Specialist?
A QI Spine Specialist is a medical expert with

Dr. Nidhi Sanghvi Shah

Dr. Shital Gaikwad

Dr. Richa Bhatia
9000 hours
of specialisation in treating back and neck conditions
32 hours
of spine physiotherapy specialisation methods in McKenzie concepts, Kinetic control, Neurodynamic solutions, Mulligan’s concepts
500 hours
and 6 months of QI Spine specialisation courses